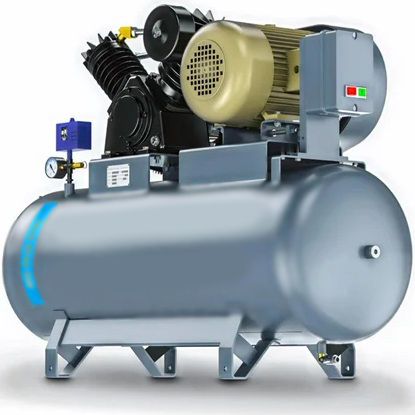


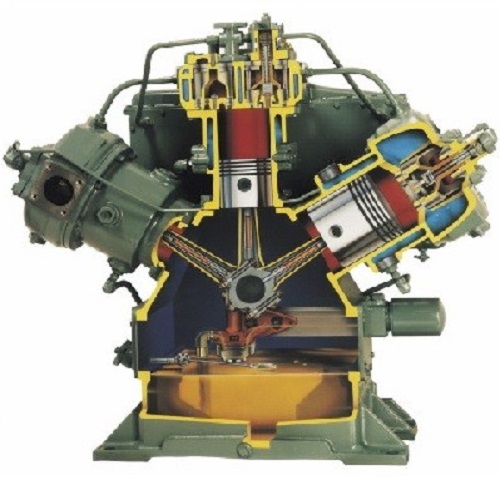
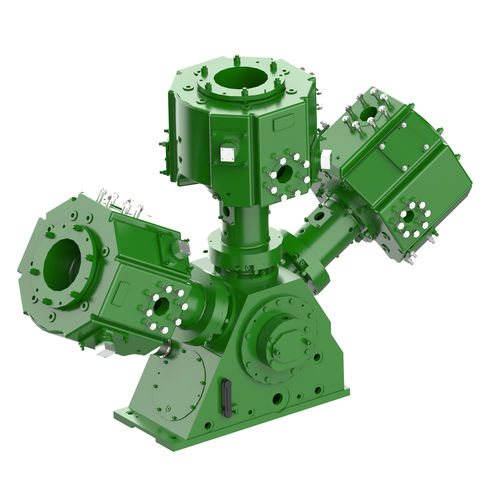
A Reciprocating Compressor or Piston Compressor is a positive-displacement compressor that uses pistons driven by a crankshaft to deliver gases at high pressure. Pressures of up to 5,000 PSIG are commonly produced by multistage reciprocating compressors. The intake gas enters the suction manifold, then flows into the compression cylinder where it gets compressed by a piston driven in a reciprocating motion via a crankshaft, and is then discharged.
Applications include railway and road vehicle air brake systems oil refineries, gas pipelines, oil and gas production drilling and well services, air and nitrogen injection, offshore platforms, chemical plants, natural gas processing plants, air conditioning, and refrigeration plants. One specialty application is the blowing of plastic bottles made of polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
There are two main types of Reciprocating Compressors compressors: Non-Lubricated and Lubricated
Non-Lubricated:
The quality of air is perfectly adapted to critical applications claiming oil-free air such as:
- food and Beverage
- electronics
- laboratories
- power industries
Energy efficient, these reliable machines provide a steady supply of compressed air 24h a day, with limited maintenance costs keeping life cycle costs to a minimum.
Lubricated:
Lubrication serves as a protective barrier between moving parts, reducing friction, and preventing excessive wear. It minimizes the heat generated during compression and ensures the efficient transfer of energy. Without adequate lubrication, reciprocating compressors can suffer from increased operating temperatures, decreased efficiency, and accelerated component wear.
